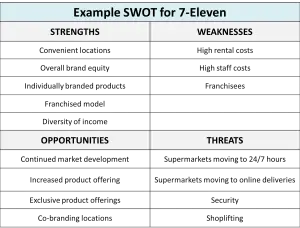
This SWOT example for 7-Eleven convenience stores is designed to help you understand and structure a SWOT analysis. It is ideal for university assignments or as a template for a business exercise.
Company Overview
7-Eleven has its head office in Dallas, Texas, USA. It was founded in 1927 and now has over 50,000 outlets worldwide.
Since the early 1990s, 7-Eleven has been controlled by Japanese interests and its parent company, Seven & I Holdings, was established as the holding company for 7-Eleven in 2005. The parent company is now ranked as the fifth largest retailer in the world. Seven and I Holdings are headquartered in Japan.
7-Eleven is a large chain of franchised convenience stores across more than 15 countries, including the USA, Canada, Japan, countries in the South-East Asia region and Australia.
The trading name of 7-Eleven was established in 1946 to reflect the then trading hours of 7am to 11pm. Since that time however, many 7-Eleven stores now trade on a 24/7 basis.
Link to their website:
Example SWOT for 7-Eleven
Strengths
Convenient locations
7-Eleven has over 50,000 outlets throughout the world, which gives them a significant location and convenience advantage. Obviously, being a convenience store, their primary benefit to consumers is that commonly purchased products are located at nearby stores. Therefore, greater market coverage through a greater number of outlets will provide increase convenience to more consumers.
Overall brand equity
7-Eleven is generally perceived as the market leader by consumers in the convenience store sector. This brand equity translates into customer loyalty and reduced price sensitivity and, therefore, continued stability of revenue streams across its outlets.
Individually branded products
In addition to having a strong overall brand, 7-Eleven also has several branded product offerings. The most famous of this are probably the Slurpee and the Big Gulp. In some countries they also have other branded offerings such as Movie Quik in the United States. These individual product brands provide a further strength to 7-Eleven, as consumers may choose to seek out these particular products/brands as their preferred choice.
Franchised model
Many of the 7-Eleven stores throughout the world are franchised. This provides to strengths for the organization – the first being that they can continue to grow the number of outlets throughout the world without having significant capital requirements, as the franchisee is typically responsible for the setup costs of the outlet – and the second advantage being that the stores are run by motivated individuals who have a profit incentive for the store to perform well.
Diversity of income
Because the overall chain of 7-Eleven operates in multiple countries, the parent company has essentially diversified its income streams across multiple markets. While this can also be a weakness, it also provides a strength of stability of income as a downturn in one particular country is unlikely to impact their overall financial results to a significant extent.
Weaknesses
High rental costs
Due to the need to locate the 7-Eleven outlets in very convenient locations, they are likely to incur higher rental costs as a result. This higher operating cost structure will mean that they will need to adopt a price premium approach. There are some consumers who are happy to pay a little bit more for convenience and speed of purchase, however other budget-conscious consumers a more price sensitive.
High staff costs
Similar to the high rental costs above, because the store operates on a 24/7 basis in some locations, this type of retailing operation is likely to have a higher ongoing operating cost structure. As a consequence of these higher costs, 7-Eleven will be required to have higher price offerings in order to protect their margins.
Franchisees
Although the overall franchised model is a strength as indicated above, running a large team of franchisees throughout the world is also a weakness. This is because it removes some element of direct control of the day-to-day operation of each outlet and passes it to the franchisee. In addition, a management team is required to recruit, train and monitor the various franchisees, which also adds to the overall cost structure on an operational basis.
Opportunities
Continued market development
As with many chains of small retailers, one of the obvious ways to grow their business is through market development. This means increasing the number of stores they have in existing markets and cities and increasing the number of countries that they operate in. While there is potential to cannibalize sales of existing outlets, much of this concern is passed to the franchisee and does not necessarily affect the parent company.
Increased product offering
In many of the 7-Eleven stores, there would be physical capacity to increase the product range and offering. This provides the opportunity of being able to offer a greater selection of both physical products, as well as services, such as ATMs, cellphone cards, and perhaps even car insurance. Certainly in some countries, 7-Eleven has expanded into offerings of wine, beer, fuel, ATMs, coffee, donuts, pizza, sandwiches and so on.
Exclusive product offerings
7-Eleven has managed to form some strong relationships with key manufacturers that have strong brands. An example here is Gatorade, where certain flavors are only offered through 7-Eleven stores. This has advantages to both of the strategic partners, and is something that will broaden the range of benefits that 7-Eleven delivers to its consumers.
Co-branding locations
7-Eleven could expand their geographic coverage through co-branded outlets with other significant retail offerings. For example, they could partner with a coffee chain or a sandwich chain and set up a co-branded store – where both stores operate independently but out of the same location. This has the advantage of attracting more consumers, who are possibly less reliant on the convenience aspect, and are likely to buy from both businesses over time.
Threats
Supermarkets moving to 24/7 hours
In some parts of the world, major supermarket chains have adopted a 24/7 operating system. It is common for most major supermarket chains to have extended hours. This erodes 7-Eleven’s natural competitive advantage of having extended shopping hours. This is a significant threat to 7-Eleven over time, as they would not have the low cost structure required to compete effectively on a price basis with a major retail chain, such as Walmart for example.
Supermarkets moving to online deliveries
Some consumers are adopting the system of ordering their groceries online and then having them delivered. Although this requires some pre-planning, it does also offer significant levels of convenience to organized consumers, which does represent a threat to 7-Eleven’s convenience-based competitive advantage.
Security
Because 7-Eleven is a convenience store that handles cash and may be open on a 24/7 basis, it is always likely to be a target for theft and armed hold-up. Obviously the chain has put in various security measures in different parts of the world, including video cameras, safes, and window barriers and so on.
Shoplifting
Like most retail stores, 7-Eleven will have the continued threat of minor shoplifting and stealing. In some locations, these stores operate on a lean budget and only have minimal staff, which presents the opportunity for some consumers to occasionally shoplift. Like with the security threat above, video cameras may assist in this regard.
Related Articles